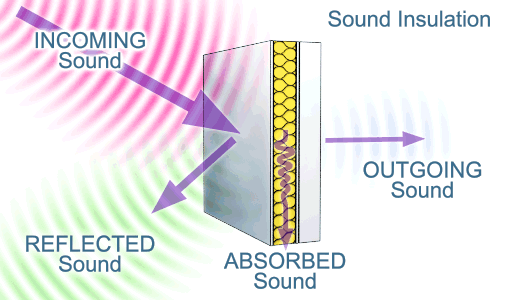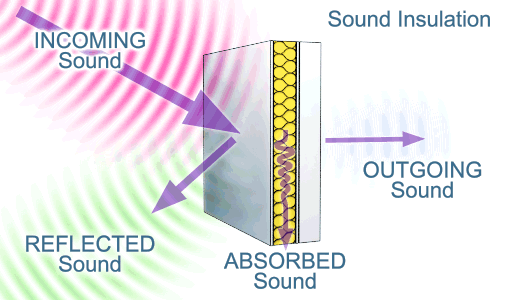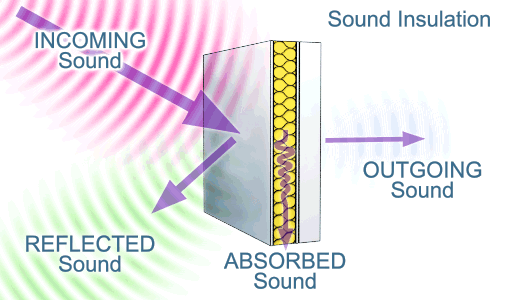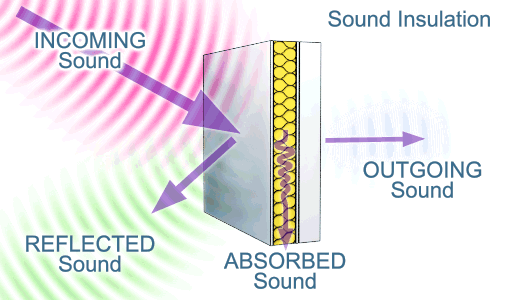
Sound Transmission
Sound Transmission Loss
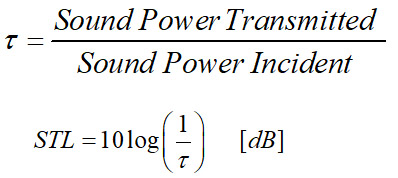
- It is defined as the ratio of sound power incident on a partition to the sound power transmitted through the partition.
- Normal incidence sound transmission loss -Two Microphone Tube
- Random incidence sound transmission loss -Reverberation Suite
Normal Incidence Sound Transmission Loss (STL) Measurement -
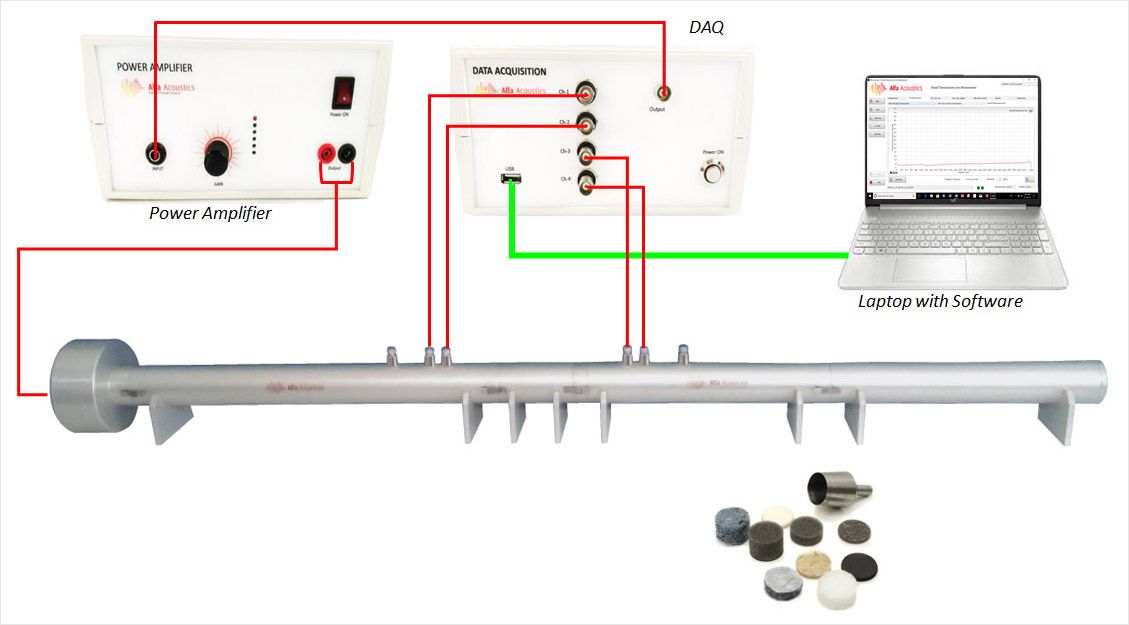
A "Normal Incidence Sound Transmission Loss (STL)" measurement is a method to determine how much sound is attenuated when passing through a material sample, where the sound waves hit the sample directly at a 90-degree angle (normal incidence), typically conducted in an impedance tube to ensure this direct wave interaction; essentially measuring the sound reduction capability of a material when sound waves hit it head-on.
The measurement is carried out based upon Transfer Matric Method as per ASTM E2611
.jpg)
This test method is similar to Test Method E1050 in that it also uses a tube with a sound source connected to one end and the test sample mounted in the tube.
For transmission loss, four microphones, at two locations on each side of the sample, are mounted so the diaphragms are flush with the inside surface of the tube perimeter. Plane waves are generated in the tube using a broadband signal from a noise source.
The resulting standing wave pattern is decomposed into forward- and backward-traveling components by measuring sound pressure simultaneously at the four locations and examining their relative amplitude and phase. The acoustic transfer matrix is calculated from the pressure and particle velocity, or equivalently the acoustic impedance, of the traveling waves on either side of the specimen.
The transmission loss, as well as several other important acoustic properties of the material, including the normal incidence sound absorption coefficient, is extracted from the transfer matrix.
Impedance Tube – Sound Transmission Loss (STL)
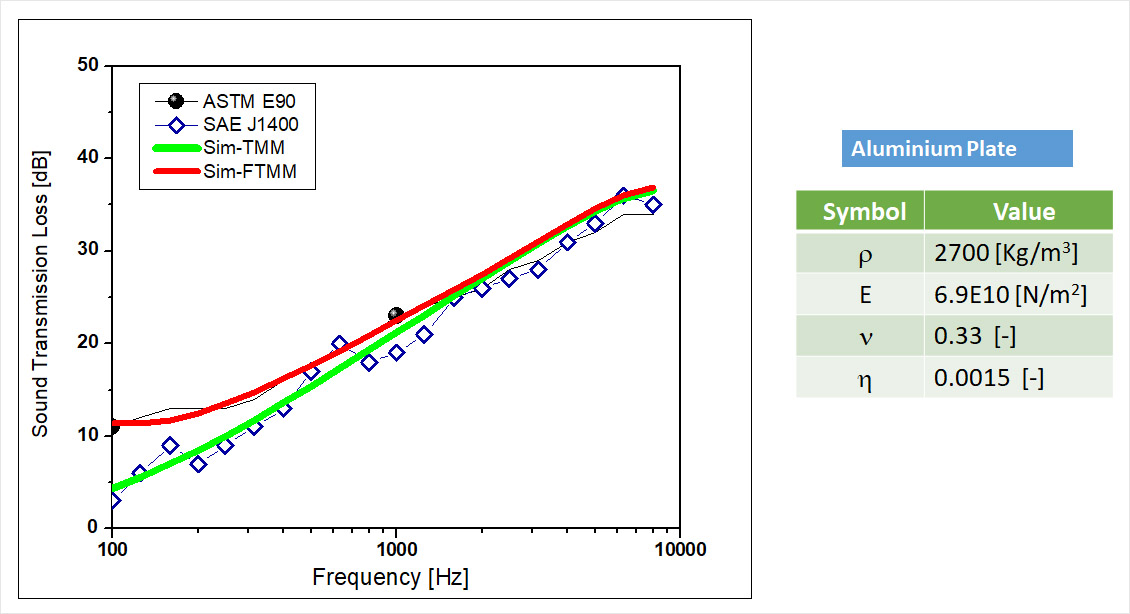
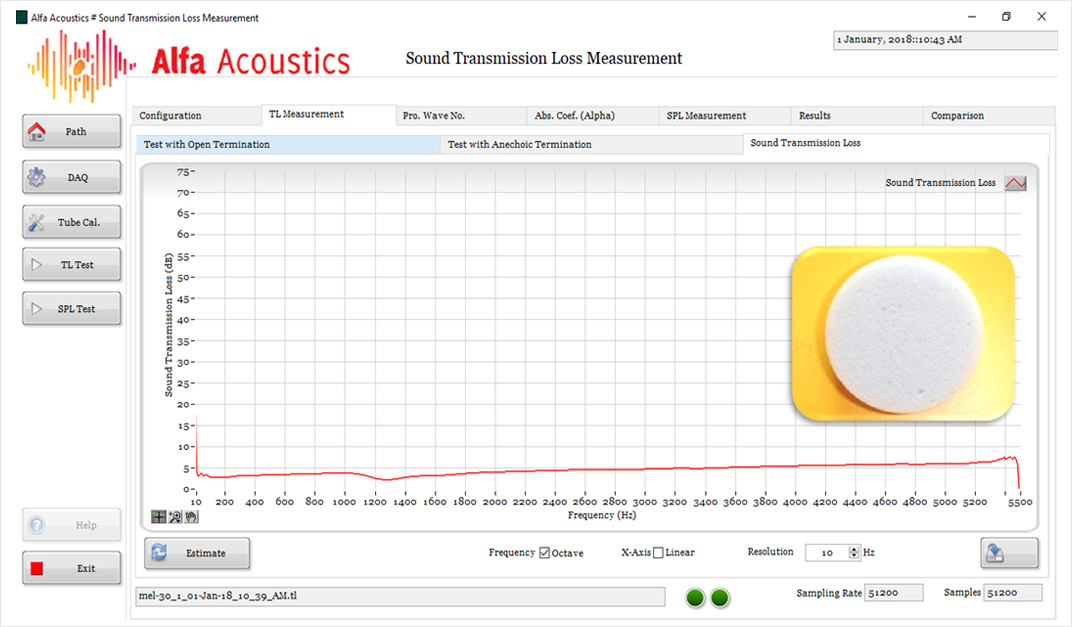
Sound Transmission Loss – Estimation
Random Incidence Sound Transmission Loss (STL) Measurement-
The random incidence transmission loss is measured in a reverberation room using the reverberant room method.
There are several standards for STL measurements and methods devised in order to directly or indirectly measure the incident and transmitted power. Typically, a so-called two-room method is used. This method has two common configurations:
- A reverberation room on the source side and the receiver side (reverberant-reverberant) – ISO 10140-2 / ASTM E90
- A reverberation room on the source side and an anechoic room on the receiver side (reverberant-anechoic)- ISO 15186 / ASTM E2249 / SAE J1400
Two Reverberation Chamber Method –
A "Two Reverberation Chamber Method" refers to a testing technique where two separate reverberation chambers are used to measure the sound transmission properties of a material or structure by placing the test sample between them, allowing for the measurement of how much sound is transmitted from one chamber to the other, essentially assessing its sound insulation capabilities; this method is particularly useful for analyzing the sound transmission loss across a material at different frequencies.
A sound source generates noise in the first chamber, which then travels through the test sample placed between the chambers and is measured in the second chamber.
By comparing the sound levels in both chambers, the transmission loss of the material can be calculated
It provides a more accurate representation of real-world sound transmission as the sound waves are diffused within the chambers, creating a random incidence sound field.
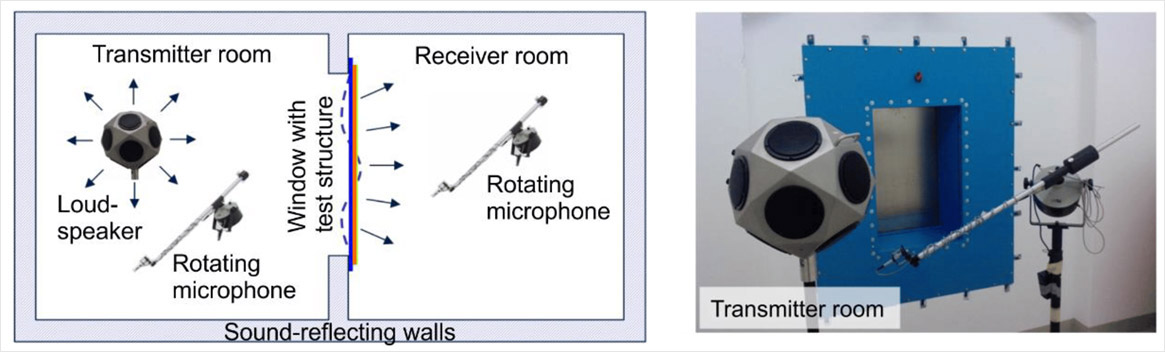
- Two adjacent reverberation rooms are arranged with an opening between them in which the test partition is installed as per ASTM E90.
- Sound Transmission loss is related to Noise reduction as
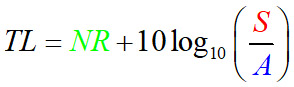
S - Area of the sample
A - Room constant of the receiving room
- Noise Reduction is simply the difference between sound pressure levels on opposite sides of a wall
SPL1 – Sound Pressure Level in the Room 1
SPL2 – Sound Pressure Level in the Room 2
Sound Transmission Class (STC ) :
- It is again a single number rating calculated in accordance with Classification E413 using values of sound transmission loss
- It provides an estimate of the performance of a partition/materials in a certain common sound insulation problems
- This is a dimensionless quantity.
- Higher is better
Sound Reduction Index-Rw
- It is used to measure the level of sound insulation provided by a structure such as a wall, window, door, or ventilator.
- It is calculated as per the standard ISO 717-1
- The Sound Transmission loss is measured as per test standards ISO 10140-2
Sound Insulation :
Reverberation and Anechoic chamber Method
This test method is part of a set for evaluating the sound transmission loss of a partition or partition element under laboratory conditions. It differs from Test Method E90 in that the sound power radiated by the element under test is measured directly using an intensity probe rather than indirectly from the space averaged receiver room sound pressure and the room reverberation time. This test method is especially useful when the receiver room requirements of Test Method E90 cannot be achieved, or flanking sound involving the receiver room surfaces is present but its influence is to be circumvented.
This test method covers the measurement of airborne sound transmission loss of building partitions such as walls of all kinds, operable partitions, floor-ceiling assemblies, doors, windows, roofs, panels and other space-dividing building elements
This method can also be used for STL measurement of Automotive components like firewall, vehicle underbody, doors panels, windshields, etc. For Automotive testing, additional test standard is SAE J1400
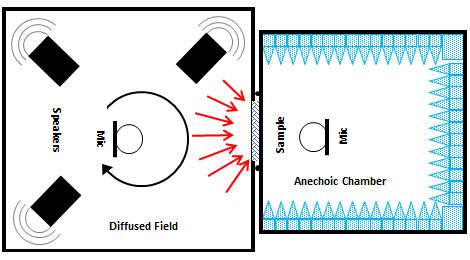
Comparison of Two STL measurement Test Methods ASTM E90 / ISO 10140 & ASTM E90 / ISO 105186-